Innovations in Healthcare Access: A Closer Look at Telehealth
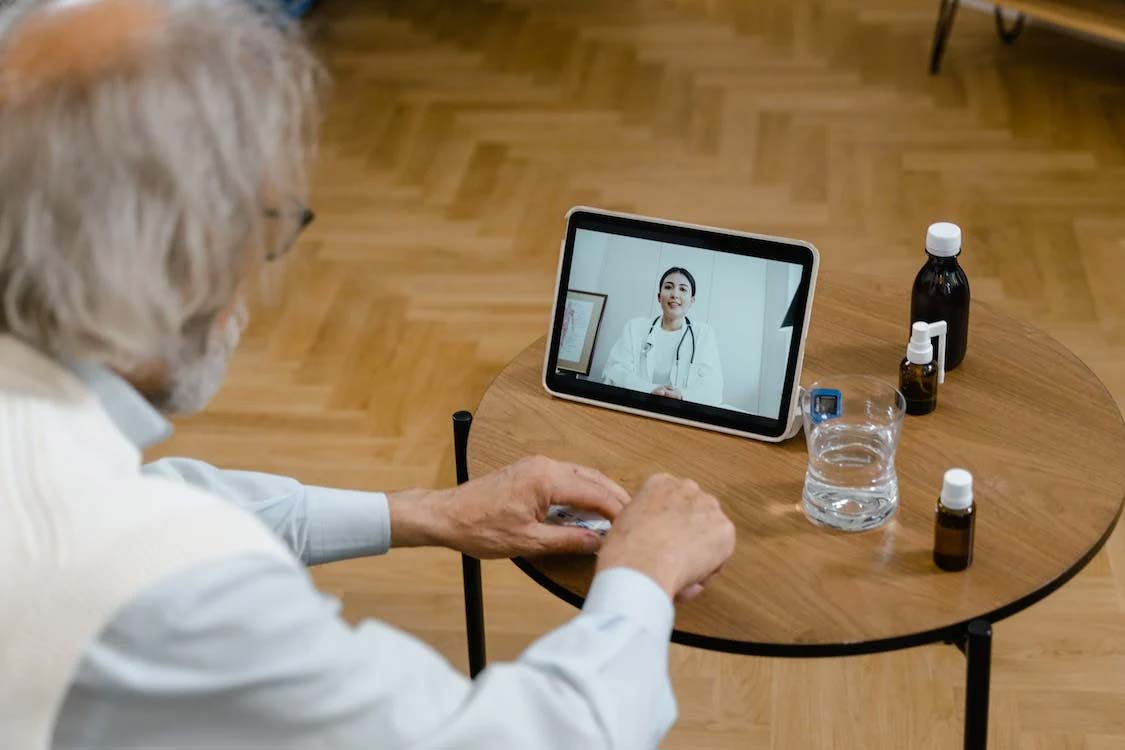

The healthcare industry is always changing, responding to the needs and limitations of a global community that is becoming more integrated. The emergence of telehealth solutions, which use technology to enable remote healthcare services, is one noteworthy trend in this industry. These developments create new opportunities for patient care, diagnosis, and treatment in addition to improving accessibility to healthcare. This essay explores how telehealth is fundamental to the new definition of healthcare access.
The rise of virtual clinics
A fundamental component of telehealth innovation are virtual clinics, which provide online consultations and testing. Patients can get real-time video consultations with qualified medical specialists on websites like anytimedoctor.co.uk. Geographical restrictions and waiting periods are removed with this healthcare model, enabling prompt treatment of urgent medical issues. Consequently, by providing a productive and efficient substitute for in-person consultations, virtual clinics are radically changing the structure of the conventional healthcare system.
Technology: The driving force
Technological developments, including fast internet access, strong data encryption methods, and advanced video conferencing capabilities, have made telehealth possible. Medical personnel can now use digital imaging, electronic health records, and other health informatics solutions to provide precise diagnosis and treatment plans. These technologies allow physicians to provide remote healthcare with the same degree of data security and quality control as in-person consultations.
Expanding the reach of specialised care
The benefits of telehealth go beyond basic healthcare to include more specialised medical care. Patients can obtain specialised care in specialities such as cardiology, dermatology, and psychiatry without leaving their homes, provided they live in distant places or are physically unable to travel. This is especially important for rural populations, which frequently lack quick access to specialised medical facilities. Telehealth is a tremendous equaliser in healthcare since it makes specialised care more accessible to all.
Regulatory considerations and ethical implications
Telehealth is facing a number of special ethical and regulatory issues as it grows more and more commonplace. Because medical records are sensitive, data privacy is a big concern. Sustaining patient trust requires secure data transmission and storage at all times. Furthermore, navigating the complex regulatory environment that differs by jurisdiction might be difficult. Regulatory organisations are creating frameworks and rules in response to this shift to maintain the security and calibre of telehealth services.
Economic benefits
In addition to directly affecting patient care, telemedicine has other financial advantages. The personnel and physical infrastructure requirements can be decreased, allowing healthcare providers to charge less for their services. These savings are frequently transferred to the patient, lowering the cost of healthcare. Furthermore, telehealth helps providers scale their operations more effectively, which helps healthcare systems struggling with growing expenses remain financially sustainable.
The future of telehealth
Telehealth is essential to healthcare’s future, not merely a band-aid or short-term fix. The potential for remote monitoring and diagnosis is anticipated to increase dramatically as wearable technology and artificial intelligence progress. These innovations will increase the personalisation of healthcare services, increasing their effectiveness and targeting.
Bridging the urban-rural divide
Telehealth’s ability to narrow the healthcare access gap between urban and rural areas is one of its most admirable features. Telehealth is essential in rural areas, where there are sometimes few and understaffed medical facilities. Telehealth can significantly enhance healthcare results in these underprivileged areas by providing remote consultations with specialists and general practitioners. For rural healthcare, getting second views or even routine checkups without being limited by distance is revolutionary.
Addressing mental health concerns
The mental health field has seen significant changes with the introduction of telehealth. There are now more options for offering mental healthcare to people who might be reluctant or unable to seek it in person, thanks to remote counselling and therapy sessions. Online consultations provide an extra degree of privacy and convenience that encourages more people to seek help, especially in light of the stigma associated with mental health. Thus, telehealth has made treatment more accessible for people in need and allowed for a more thorough approach to mental health.
Conclusion
One ground-breaking invention that has completely changed the delivery and accessibility of healthcare services is telehealth. Telehealth has improved healthcare affordability, efficiency, and equity by offering a range of assistive technology, virtual clinics, and specialised remote consultations. There is little doubt that telehealth will play a crucial role in determining the direction of global healthcare as we look ahead to its ongoing development.
Image attributed to Pexels.com